mega cisterna magna versus arachnoid cyst|Mega Cisterna Magna (MCM) and Arachnoid Cysts (AC) : Bacolod The term was coined by the Belgian neurosurgeon Richard Gonsette (1929-2014)8in 1962, in patients with cerebellar atrophy 7. Tingnan ang higit pa Tuesday at 9:45 AM, the premier gold Baba Ijebu result for today is a 5-digit lottery, meaning players choose 5 numbers from 1 to 90. The winning numbers are drawn randomly, and players win if their numbers match the winning numbers in any order. . Premier King. Saturday at 9:45 AM, Amid the diverse tapestry of Nigerian .
PH0 · Retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst
PH1 · Mega cisterna magna
PH2 · Mega Cisterna Magna and Retrocerebellar Arachnoid Cysts
PH3 · Mega Cisterna Magna (MCM) and Arachnoid Cysts (AC)
PH4 · Mega Cisterna Magna
PH5 · Management of Arachnoid Cysts: A Comprehensive Review
PH6 · Is it an arachnoid cyst or a mega cisterna magna? What to and
PH7 · Arachnoid cyst
PH8 · Arachnoid Cysts: What Are They, Location, Causes & Symptoms
PH9 · Arachnoid Cyst Imaging
Who is Burlington Industries Philippines. Burlington Industries Philippines, Inc. is the trademark owner in the Philippines of the following socks brands Burlington, BioFresh, Puma, Bally, Camp and Knit. The company manufactures full range of designs for sports socks, dress socks, and casual socks for men, trouser socks, foot cover and stockings .As a world leading gaming brand, MSI is the most trusted name in gaming and eSports. We stand by our principles of breakthroughs in design, and roll out the amazing gaming gear like motherboards, graphics cards, laptops and desktops.
mega cisterna magna versus arachnoid cyst*******Mega cisterna magna needs to be distinguished from other causes of an enlarged retrocerebellar CSF space: 1. arachnoid cyst: can be difficult to distinguish from a mega cisterna magna 2. epidermoid cyst: often shows a heterogeneous/dirty signal on FLAIR and restricted diffusion 3. cerebellar . Tingnan ang higit paA mega cisterna magna is thought to occur in ~1% of all brains imaged postnatally. It constitutes 54% of all cystic posterior fossa malformations 4. Especially if noted antenatally, a mega cisterna magna has been associated with: 1. infarction . Tingnan ang higit pa
Some authors have proposed that mega cisterna magna is a result of a delayed Blake pouch fenestration; when fenestration does not occur, it results in a Blake . Tingnan ang higit paThe term was coined by the Belgian neurosurgeon Richard Gonsette (1929-2014)8in 1962, in patients with cerebellar atrophy 7. Tingnan ang higit paOn antenatal ultrasound, mega cisterna magna refers to an enlarged retrocerebellar CSF space: 1. usually >10 mm (some . Tingnan ang higit pa There is debate as to whether mega cisterna magna (MCM) arises from a pathologic insult; recent evidence suggests that it may be on the mildest end of the . Mega cisterna magna refers to a cystic posterior fossa malformation that is characterized by an enlarged cisterna magna, absence of hydrocephalus, and an intact cerebellar vermis. It must be .mega cisterna magna lacks a compression or a mass effect upon the cerebellum. the presence of signal void vascular structure within or next to the CSF space favors mega cisterna magna. scalloping of the adjacent .
Arachnoid cysts usually grow on the brain (intracranial arachnoid cysts). Less commonly, they grow on the spinal cord (spinal arachnoid cysts). Both types .
mega cisterna magna versus arachnoid cyst Mega Cisterna Magna (MCM) and Arachnoid Cysts (AC) As several surgical management options exist, we explore the best approach according to each major type of arachnoid cyst: middle cranial fossa cyst, suprasellar .What are mega cisterna magna (MCM) and arachnoid cysts (AC)? MCM involves the enlargement of normal fluid-filled space in the brain with no other structural differences . Arachnoid cysts are relatively common benign and asymptomatic lesions occurring in association with the central nervous system, both within the intracranial compartment (most common) as . A large cisterna magna (mega cisterna magna) occasionally may be confused with an arachnoid cyst. Mega cisterna magna may represent a normal variant (intact cerebellum and.Is it an arachnoid cyst or a mega cisterna magna? What to and where to look for to make the correct diagnosis? Congress: ECR 2018. Poster Number: C-1854. Type: Educational .
Mega cisterna magna is the enlarged cisterna magna (more than 10 mm in mid-sagittal plane) with intact cerebellar vermis and normal fourth ventricle. It freely communicates with the subarachnoid .

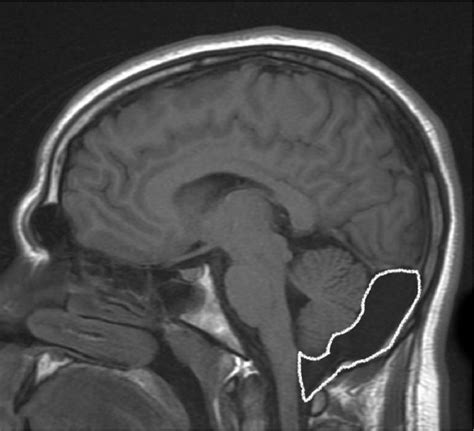
One of the supportive findings for the diagnosis of mega cisterna magna is the presence of internal lines crossing inside the cistern representing folds of the arachnoid membrane. These folds are virtually never seen in any similar lesion like a retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst or Dandy-Walker malformation. 1 article features images from this . Cystic or cyst-like malformations of the posterior fossa represent a spectrum of disorders, including the Dandy-Walker malformation, vermian-cerebellar hypoplasia, mega cisterna magna, and arachnoid cyst. Differentiation of these lesions may be difficult with routine cross-sectional imaging; however, an accurate diagnosis is . cisterna magna (need to be distinguished from a mega cisterna magna) cerebellopontine angle (need to be distinguished from an epidermoid cyst) spinal canal (see spinal arachnoid cysts) CT. Arachnoid cysts are extremely well circumscribed, with an imperceptible wall, and displace adjacent structures. Mega cisterna magna needs to be distinguished from other causes of an enlarged retrocerebellar CSF space: arachnoid cyst: can be difficult to distinguish from a mega cisterna magna; epidermoid cyst: often shows a heterogeneous/dirty signal on FLAIR and restricted diffusion; cerebellar atrophy / cerebellar hypoplasiaWhat are mega cisterna magna (MCM) and arachnoid cysts (AC)? MCM involves the enlargement of normal fluid-filled space in the brain with no other structural differences anomaly in other cerebral structures. ACs are usually benign, cerebro-spinal fluid-like collections that develop within the layers of the membranes that wrap the brain. It is an extra-axial collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) delineated by arachnoid that does not directly communicate with the ventricular system or the subarachnoid space. Retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst pushes the vermis forward, whereas an MCM pushes the vermis up from foramen magnum. 1 , 2 , 3. Midline arachnoid cyst .
An enlarged posterior fossa 'CSF' space posterior to the cerebellum has a number of differentials that include: mega cisterna magna. epidermoid cyst. arachnoid cyst. Careful attention to the cerebellum needs to paid as also to be considered are: cerebellar atrophy. Dandy-Walker malformations. [Show full abstract] cystic structure originating within the roof of the 4th ventricle that herniates into the cisterna magna, and posterior fossa arachnoid cysts, which typically displace both .
Although differential of retrocerebellar arachnoid cysts and mega cisterna magna is of little clinical concern, as both lesions are mostly asymptomatic and require no follow-up, they are both frequently encountered lesions in clinical practice, as almost always incidental findings, that has different causative mechanisms and embryonic origins.mega cisterna magna versus arachnoid cystReview of literature shows various authors have classified the arachnoid cysts.[1,2,5] With regards to the PFAC, . which they had reported and that included mega cisterna magna (11 cases), Dandy-Walker malformation (5 cases) and others (3 cases). In these 7 cases, multiple surgical procedures like resection of the posterior wall of the cyst .
Mega cisterna magna refers simply to focal enlargement of the cisterna magna, the biggest of the subarachnoid cisterns, which is located posterior and inferior to cerebellum and dorsal surface of the brain stem, medulla oblongata, and superior to foramen magnum. [1] The most accepted quantitative measurement of the enlargement is more than 10 .Mega Cisterna Magna (MCM) and Arachnoid Cysts (AC) A large cisterna magna (mega cisterna magna) occasionally may be confused with an arachnoid cyst. Mega cisterna magna may represent a normal variant (intact cerebellum and vermis), .Cystic or cyst-like malformations of the posterior fossa represent a spectrum of disorders, including the Dandy-Walker malformation, vermian-cerebellar hypoplasia, mega cisterna magna, and arachnoid cyst. Differentiation of these lesions may be difficult with routine cross-sectional imaging; however . Blake's pouch cyst is a cystic appearing structure that represents posterior ballooning of the inferior medullary velum into the cisterna magna, below and posterior to the vermis , that communicates with an open fourth ventricle. It is caused by a failure of the regression of Blake's pouch secondary to the non-perforation of the foramen of .
Cisterna Magna. Mega cisterna magna is a developmental variation of the posterior fossa characterized by a prominent, enlarged cisterna magna that freely communicates with the perimedullary subarachnoid space. . The condition should be differentiated from the Dandy-Walker complex, cerebellar hypoplasia and posterior fossa arachnoid cyst. 111.How do MCM and AC cysts happen? Both are considered cystic lesions of the posterior brain. In the early development of the fetus an alteration occurs in the making of the system and spaces where the spinal fluid normally travels, and mega cisterna magna results as a consequence of the accumulation of spinal fluid in this space. The remainder may occur in the cerebellopontine angle, suprasellar and quadrigeminal cisterns, cerebral convexities, and cisterna magna [2, 8]. Due to the possibility of compression of neurovascular structures by large arachnoid cysts (Figure (Figure1), 1), a surgical approach is preferable to passive observation, as is done with .
Listen to music by Moses Koul on Apple Music. Find top songs and albums by Moses Koul including Summer Walk (feat. Moses Koul), Shobdohin (feat. Moses Koul) and more.
mega cisterna magna versus arachnoid cyst|Mega Cisterna Magna (MCM) and Arachnoid Cysts (AC)